How Do Inherited IRA's Work For Non-Spouse Beneficiaries?
The SECURE Act was signed into law on December 19, 2019 which completely changed the distribution options that are available to non-spouse beneficiaries. One of the major changes was the elimination of the “stretch provision” which previously allowed non-spouse beneficiaries to rollover the balance into their own inherited IRA and then take small
The SECURE Act was signed into law on December 19, 2019 which completely changed the distribution options that are available to non-spouse beneficiaries. One of the major changes was the elimination of the “stretch provision” which previously allowed non-spouse beneficiaries to rollover the balance into their own inherited IRA and then take small required minimum distributions over their lifetime.
That popular option was replaced with the new 10 Year Rule which will apply to most non-spouse beneficiaries that inherit IRA’s and other types of retirements account after December 31, 2019.
New Rules For Non-Spouse Beneficiaries Years 2020+
The article and Youtube video listed below will provide you with information on:
New distribution options available to non-spouse beneficiaries
The new 10 Year Rule
Beneficiaries that are grandfathered in under the old rules
SECURE Act changes
Old rules vs New rules
New tax strategies for non-spouse beneficiaries
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Required Minimum Distribution Tax Strategies
If you are turning age 72 this year, this article is for you. You will most likely have to start taking required minimum distributions from your retirement accounts. This article will outline:
If you are turning age 72 this year, this article is for you. You will most likely have to start taking required minimum distributions from your retirement accounts. This article will outline:
Deadlines to take your RMD
Tax implications
Strategies to reduce your tax bill
How is my RMD calculated?
The IRS has a tax table that determines the amount that you have to take out of your retirement accounts each year. To determine your RMD amount you will need to obtain the December 31st balance in your retirement accounts, find your age on the IRS RMD tax table, and divide your 12/31 balance by the number listed next to your age in the tax table.
Exceptions to the RMD requirement........
There are two exceptions. First, Roth IRA’s do not require RMD’s. Second, if you are still working, you maintain a balance in your current employer’s retirement plan, and you are not a 5%+ owner of the company, you do not need to take an RMD from that particular retirement account until you terminate employment with the company. Which leads us to the first tax strategy. If you are age 72 or older and you are still working, you can typically rollover your traditional IRA’s and former employer 401(k)/403(b) accounts into your current employers retirement plan. By doing so, you avoid the requirement to take RMD’s from those retirement accounts outside of your current employers retirement plan and you avoid having to pay taxes on those required minimum distributions. If you are 5%+ owner of the company, you are out of luck. The IRS will still require you to take the RMD from your retirement account even though you are still “employed” by the company.
Deadlines
In the year that you turn 72, if you do not meet one of the exceptions listed above, you will have a very important decision to make. You have the option to take the RMD by 12/31 of that year or wait until the beginning of the following tax year. For your first RMD, the deadline to take the RMD is April 1st of the year following the year that you turn age 72. For example, if you turn 72 on June 2017, you will not be required to take your first RMD until April 1, 2018. If you worked full time from January 2017 – June 2017, it may make sense for you to delay your first RMD until January 2018 because your income will most likely be higher in 2017 because you worked for half of the year. When you take a RMD, like any other distribution from a pre-tax retirement account, it increases the amount of your taxable income for the year. From a pure tax standpoint it usually makes snese to realize income from retirement accounts in years that you are in a lower tax bracket.
SPECIAL NOTE: If you decided to delay your first RMD until after December 31st, you will be required to take two RMD’s in that year. One prior to April 1st and the second before Decemeber 31st. The April 1st rule only applies to your first RMD. You should consult with your accountant to determine the best RMD strategy given your personal income tax situation. For all tax years following the year that you turn age 72, the RMD deadline is December 31st.
VERY IMPORTANT: Do not miss your RMD deadline. The IRS hits you with a lovely 50% excise tax if you fail to take your RMD by the deadline. If you were due a $4,000 RMD and you miss the deadline, the IRS is going to levy a $2,000 excise tax against you.
Contributions to charity to avoid taxes
Another helpful tax strategy, if you make contributions to a charity, a church, or not-for-profit organization, you have the option with IRA’s to direct all or a portion of your RMD directly to these organization. In doing so, you satisfy your RMD but avoid having to pay income tax on the distribution from the IRA. The number one rule here, the distribution must go directly from your IRA account to the not-for-profit organization. At no point during this transaction can the owner of the IRA take possession of cash from the RMD otherwise the full amount will be taxable to the owner of the IRA. Typically the custodian of your IRA will have to issue and mail a third party check directly to the not-for-profit organization.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Tax Secret: Spousal IRAs
Spousal IRA’s are one of the top tax tricks used by financial planners to help married couples reduce their tax bill. Here is how it works:
Spousal IRA’s are one of the top tax tricks used by financial planners to help married couples reduce their tax bill. Here is how it works:
In most cases you need “earned income” to be eligible to make a contribution to an Individual Retirement Account (“IRA”). The contribution limits for 2021 is the lesser of 100% of your AGI or $6,000 for individuals under the age of 50. If you are age 50 or older, you are eligible for the $1,000 catch-up making your limit $7,000.
There is an exception for “Spousal IRAs” and there are two cases where this strategy works very well.
Case 1: One spouse works and the other spouse does not. The employed spouse is currently maxing out their contributions to their employer sponsored retirement plan and they are looking for other ways to reduce their income tax liability.
If the AGI (adjusted gross income) for that couple is below $198,000 in 2021, the employed spouse can make a contribution to a Spousal Traditional IRA up to the $6,000/$7,000 limit even though their spouse had no “earned income”. It should also be noted that a contribution can be made to either a Traditional IRA or Roth IRA but the contributions to the Roth IRA do not reduce the tax liability because they are made with after tax dollars.
Case 2: One spouse is over the age of 70 ½ and still working (part time or full time) while the other spouse is retired. IRA rules state that once you are age 70½ or older you can no longer make contributions to a traditional IRA. However, if you are age 70½ or older BUT your spouse is under the age of 70½, you still can make a pre-tax contribution to a traditional IRA for your spouse.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Traditional vs. Roth IRA’s: Differences, Pros, and Cons
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRA’s) are one of the most popular retirement vehicles available for savers and the purpose of this article is to give a general idea of how IRA’s work, explain the differences between Traditional and Roth IRA’s, and provide some pros and cons of each. In January 2015, The Investment Company Institute put out a research
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRA’s) are one of the most popular retirement vehicles available for savers and the purpose of this article is to give a general idea of how IRA’s work, explain the differences between Traditional and Roth IRA’s, and provide some pros and cons of each. In January 2015, The Investment Company Institute put out a research report with some interesting statistics regarding IRA’s which can be found at the following link, ICI Research Perspective. The article states, “In mid-2014, 41.5 million, or 33.7 percent of U.S. households owned at least one type of IRA”. At first I was slightly shocked and asked myself the following question: “If IRA’s are the most important investment vehicle and source of income for most retirees, how do only one third of U.S. households own one?” Then when I took a step back and considered how money gets deposited into these retirement vehicles this figure begins making more sense.
Yes, a lot of American’s will contribute to IRA’s throughout their lifetime whether it is to save for retirement throughout one’s lifetime or each year when the CPA gives you the tax bill and you ask “What can I do to pay less?” When thinking about IRA’s in this way, one third of American’s owning IRA’s is a scary figure and leads one to believe more than half the country is not saving for retirement. This is not necessarily the case. 401(k) plans and other employer sponsored defined contribution plans have become very popular over the last 20 years and rather than individuals opening their own personal IRA’s, they are saving for retirement through their employer sponsored plan.
Employees with access to these employer plans save throughout their working years and then, when they retire, the money in the company retirement account will be rolled into IRA’s. If the money is rolled directly from the company sponsored plan into an IRA, there is likely no tax or penalty as it is going from one retirement account to another. People roll the balance into IRA’s for a number of reasons. These reasons include the point that there is likely more flexibility with IRA’s regarding distributions compared to the company plan, more investment options available, and the retiree would like the money to be managed by an advisor. The IRA’s allow people to draw on their savings to pay for expenses throughout retirement in a way to supplement income that they are no longer receiving through a paycheck.
The process may seem simple but there are important strategies and decisions involved with IRA’s. One of those items is deciding whether a Traditional, Roth or both types of IRA’s are best for you. In this article we will breakdown Traditional and Roth IRA’s which should illustrate why deciding the appropriate vehicle to use can be a very important piece of retirement planning.
Why are they used?
Both Traditional and Roth IRA’s have multiple uses but the most common for each is retirement savings. People will save throughout their lifetime with the goal of having enough money to last in retirement. These savings are what people are referring to when they ask questions like “What is my number?” Savers will contribute to retirement accounts with the intent to earn money through investing. Tax benefits and potential growth is why people will use retirement accounts over regular savings accounts. Retirees have to cover expenses in retirement which are likely greater than the social security checks they receive. Money is pulled from retirement accounts to cover the expenses above what is covered by social security. People are living longer than they have in the past which means the answer to “What is my number?” is becoming larger since the money must last over a greater period.
How much can I contribute?
For both Traditional and Roth IRA’s, the limit in 2021 for individuals under 50 is the lesser of $6,000 or 100% of MAGI and those 50 or older is the lesser of $7,000 or 100% of MAGI. More limit information can be found on the IRS website Retirement Topics - IRA Contribution Limits
What are the important differences between Traditional and Roth?
Taxation
Traditional (Pre-Tax) IRA: Typically people are more familiar with Traditional IRA’s as they’ve been around longer and allow individuals to take income off the table and lower their tax bill while saving. Each year a person contributes to a Pre-Tax IRA, they deduct the contribution amount from the income they received in that tax year. The IRS allows this because they want to encourage people to save for retirement. Not only are people decreasing their tax bill in the year they make the contribution, the earnings of Pre-Tax IRA’s are not taxed until the money is withdrawn from the account. This allows the account to earn more as money is not being taken out for taxes during the accumulation phase. For example, if I have $100 in my account and the account earns 10% this year, I will have $10 of earnings. Since that money is not taxed, my account value will be $110. That $110 will increase more in the following year if the account grows another 10% compared to if taxes were taken out of the gain. When the money is used during retirement, the individual will be taxed on the amount distributed at ordinary income tax rates because the money was never taxed before. A person’s tax rate during retirement is likely to be lower than while they are working because total income for the year will most likely be less. If the account owner takes a distribution prior to 59 ½ (normal retirement age), there will be penalties assessed.
Roth (After-Tax) IRA: The Roth IRA was established by the Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997. Unlike the Traditional IRA, contributions to a Roth IRA are made with money that has already been subject to income tax. The money gets placed in these accounts with the intent of earning interest and then when the money is taken during retirement, there is no taxes due as long as the account has met certain requirements (i.e. has been established for at least 5 years). These accounts are very beneficial to people who are younger or will not need the money for a significant number of years because no tax is paid on all the earnings that the account generates. For example, if I contribute $100 to a Roth IRA and the account becomes $200 in 15 years, I will never pay taxes on the $100 gain the account generated. If the account owner takes a distribution prior to 59 ½ (normal retirement age), there will be penalties assessed on the earnings taken.
Eligibility
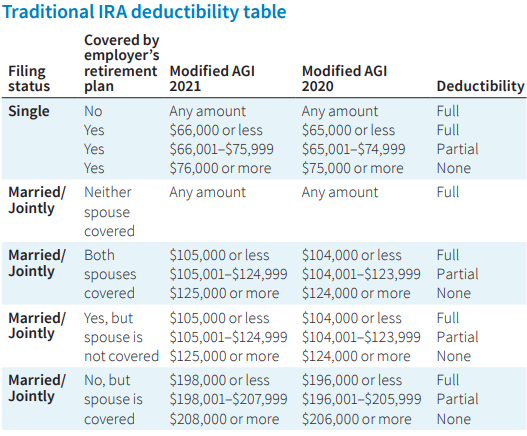
Traditional IRA: Due to the benefits the IRS allows with Traditional IRA’s, there are restrictions on who can contribute and receive the tax benefit for these accounts. Below is a chart that shows who is eligible to deduct contributions to a Traditional IRA:
There are also Required Minimum Distributions (RMD’s) associated with Pre-Tax dollars in IRA’s and therefore people cannot contribute to these accounts after the age of 70 ½. Once the account owner turns 70 ½, the IRS forces the individual to start taking distributions each year because the money has never been taxed and the government needs to start receiving revenue from the account. If RMD’s are not taken timely, there will be penalties assessed.
Roth IRA: As long as an individual has earned income, there are only income limitations on who can contribute to Roth IRA’s. The limitations for 2021 are as follows:
There are a number of strategies to get money into Roth IRA’s as a financial planning strategy. This method is explained in our article Backdoor Roth IRA Contribution Strategy.
Investment Strategies
Investment strategies are different for everyone as individuals have different risk tolerances, time horizons, and purposes for these accounts.
That being said, Roth IRA’s are often times invested more aggressively because they are likely the last investment someone touches during retirement or passes on to heirs. A longer time horizon allows one to be more aggressive if the circumstances permit. Accounts that are more aggressive will likely generate higher returns over longer periods. Remember, Roth accounts are meant to generate income that will never be taxed, so in most cases that account should be working for the saver as long as possible. If money is passed onto heirs, the Roth accounts are incredibly valuable as the individual who inherits the account can continue earning interest tax free.
Choosing the correct IRA is an important decision and is often times more complex than people think. Even if you are 30 years from retiring, it is important to consider the benefits of each and consult with a professional for advice.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Inherited IRA's: How Do They Work?
An Inherited IRA is a retirement account that is left to a beneficiary after the owner’s death. It is important to have a general knowledge of how Inherited IRA’s work because a minor error in how the account is set up could lead to major tax consequences.
An Inherited IRA is a retirement account that is left to a beneficiary after the owner’s death. It is important to have a general knowledge of how Inherited IRA’s work because a minor error in how the account is set up could lead to major tax consequences.
Before going into the different kinds of Inherited IRA’s, if you are the sole beneficiary of your spouse’s IRA, you are able to transfer the assets to your own existing IRA or to a new IRA through what is called a “Spousal Transfer”. This account is not treated as an Inherited IRA and therefore is subject to all the rules a Traditional IRA would be subject to as if it was always held in your name. If the spouse needs to have access to the money before age 59 ½, it would probably make sense to set up an Inherited IRA because this would give the spouse options to access the money without incurring a 10% early withdrawal penalty.
Withdrawal Rules for Spouse & Non-Spouse Beneficiaries
The SECURE Act that passed in December 2019 dramatically changed the distribution options that are available to non-spouse beneficiaries. If you are spousal beneficiary please reference the following article:
10 Year Method
All the assets must be distributed by the 10th year after the year in which the account holder died. This option may make sense compared to the Lump Sum option explained next to spread out the tax liability over a longer period.
Lump Sum Distribution
You may take a lump sum distribution when the account is inherited. It is recommended that you consult your tax preparer to discuss the tax consequences of this method since you may move up into a different tax bracket.
Additional Takeaways
If the decedent was required to take a distribution in the year of death, it is important to determine whether or not the decedent took the distribution. If the decedent was required to take a RMD but did not do so in the year they passed, the inheritor must take the distribution based on the life expectancy of the decedent or the distribution will be subject to a 50% penalty. Distributions going forward will be based on the life expectancy of the inheritor.
It is important to be sure a beneficiary form is completed for the Inherited IRA. If there is no beneficiary and the account goes to an estate then the inheritor will have limited choices on which distribution method to choose among other tax consequences.
You are only able to combine Inherited IRA’s if they were inherited from the same individual. If you have multiple Inherited IRA’s from different individuals, you cannot commingle the assets because of the distributions that must be taken.
There is no 60 day rule with Inherited IRA’s like there is with other Traditional IRA’s. The 60 day rule allows someone to withdraw money from an IRA and as long as it’s replenished within 60 days there is no tax consequence. This is not available with Inherited IRA’s, all non-Roth distributions are taxable.
The charts below are from insurancenewsnet.com publication titled “Extended IRA Quick Reference Guide” give another look at the details of Inherited IRA’s.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Backdoor Roth IRA Contribution Strategy
This strategy is for high income earners that make too much to contribute directly to a Roth IRA. In recent years, some of these high income earners have been implementing a “backdoor Roth IRA conversion strategy” to get around the Roth IRA contribution limitations and make contributions to Roth IRA’s via “conversions”. For the 2020 tax year, your
This strategy is for high income earners that make too much to contribute directly to a Roth IRA. In recent years, some of these high income earners have been implementing a “backdoor Roth IRA conversion strategy” to get around the Roth IRA contribution limitations and make contributions to Roth IRA’s via “conversions”. For the 2021 tax year, your ability to make contributions to a Roth IRA begins to phase out at the following AGI thresholds based on your filing status:
Single: $125,000
Married Filing Jointly: $198,000
Married Filing Separately: $0
However, in 2010 the IRS removed the income limits on “IRA Conversions” which open up an opportunity……if executed correctly…….for high income earners to make “backdoor” contributions to a Roth IRA.
Why would a high income earning want to contribute to a Roth IRA? Once high income earners have maxed out their contributions to their employer sponsored retirement plans, they usually begin to fund plain vanilla investment management accounts or whole life insurance policies. When assets accumulate in an investment management account, once liquidated, the account owner typically has to pay either short-term or long term capital gains on the appreciation. For whole life insurance, even though the accumulation is tax deferred, if the policy is surrendered, the policy owner pays ordinary income tax on the gain in the policy.
With a Roth IRA, after tax contributions are made to the account and the gains in the account are withdrawn TAX FREE if the account owner at the time of withdrawal is over the age of 59½ and the Roth IRA has been in existence for 5 years. A huge tax benefit for high income earners who are typically in a medium to higher tax bracket even in retirement.
Here is how the strategy works
Rollover all existing pre-tax IRA’s into your employer sponsored retirement plan
Make a non-deductible contribution to a Traditional IRA
Convert the Traditional IRA to a Roth IRA
Here are the pitfalls in the execution process
Over the years, more and more individuals have become aware of this wealth accumulation strategy. However, there are risks associated with executing this strategy and if not executed correctly could result in adverse tax consequences.
Here are the top pitfalls:
Forget to aggregate Pre-Tax IRA’s
Do not understand that SEP IRA’s and Simple IRA’s are included in the Aggregation Rule
They create a “step transaction”
Pitfall #1: IRS Aggregation Rule
The IRA aggregate rule stipulates that when an individual has multiple IRAs, they will allbe treated as one account when determining the tax consequences of any distributions (including a distribution out of the account for a Roth conversion).
This creates a significant challenge for those who wish to do the backdoor Roth strategy, but have otherexisting IRA accounts already in place (e.g., from prior years’ deductible IRA contributions, or rollovers from prior 401(k) and other employer retirement plans). Because the standard rule for IRA distributions (and Roth conversions) is that any after-tax contributions come out along with any pre-tax assets (whether from contributions or growth) on a pro-rata basis, when all the accounts are aggregated together, it becomes impossible to justconvert the non-deductible IRA.
If an individual has pre-tax IRA’s we typically recommend that they rollover those IRA’s into their employer sponsored retirement plans which eliminates all of their pre-tax IRA balance and then open the opportunity to execute this backdoor Roth IRA contribution strategy.
Pitfall #2: SEP IRA & Simple IRA's count
Many smaller companies and self-employed individuals sponsor SEP IRA’s or Simple IRA Plans. Many individuals just assume that these are “employer sponsored retirement plans” not subject to the aggregation rules. Wrong. In the eyes of the IRS these are “pre-tax IRA’s” and are subject to the aggregation rules. If you have a Simple IRA or SEP IRA, make sure you take this common pitfall into account.
Pitfall #3: Beware IRS Step Transaction Rule
This is probably the most common pitfall that we see when executing this strategy. Individuals and investment advisors alike will make deposits to the non-deductible traditional IRA and then the next day process the conversion to the Roth IRA. In doing this, you run the risk of creating a “step transaction”.
There is a very long explanation tied to “step transactions” and how to avoid a “step transactions” but I will provide you with a brief summary of the concept.
Here it is, if you use legal loop holes in the tax system in an obvious effort to side step other IRS limitations (like the Roth IRA income limit) it could be considered a “step transaction” by the IRS and the IRS may disallow the conversion and assess tax penalties.
Disclosure: Backdoor Roth IRA Conversion Strategy
It is highly recommend that you work closely with your financial advisor and tax advisor to determine whether or not this is a viable wealth accumulation strategy based on your personal financial situation.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
What is the 60 Day Rule and How Should it be Used?
The 60 day rule refers to the length of time an individual has to deposit money back into a retirement account that was previously withdrawn without incurring a taxable event. There are a number of reasons someone would withdraw money from an account whether it be to pay a large tax bill, obtain cash for an unexpected expense, or to rollover the
The 60 day rule refers to the length of time an individual has to deposit money back into a retirement account that was previously withdrawn without incurring a taxable event. There are a number of reasons someone would withdraw money from an account whether it be to pay a large tax bill, obtain cash for an unexpected expense, or to rollover the balance into another retirement account.
There are multiple ways to rollover a balance from one retirement account to another so we will begin by explaining the more common ways to rollover a balance where the 60 day rule won't come into play.
Direct Rollover
A direct rollover is a transfer from a retirement plan to another retirement plan or IRA where the custodian of your current plan makes payment directly to your new account. This can be in the form of a check made payable to the new account custodian or a direct wire transfer. This method will avoid taxes and penalties because the account owner never had access to the cash during the transfer.
Trustee to Trustee Transfer
Similar to the direct rollover, a trustee to trustee transfer moves money from one IRA to another IRA without the account owner ever having access to the cash and therefore avoiding taxes and penalties.
The direct rollover and trustee to trustee transfer methods both avoid taxes and penalties as cash is never available to the owner and therefore the 60 day rule does not come into effect. In any case where the account owner has access to the cash, the money will have to be redeposited into another retirement account within 60 days or the owner will be taxed on any pre-tax dollars and possibly penalized if the owner is under the age of 59 ½.
The 60 day rule is one of the only ways an owner has access to money in a retirement account without paying taxes or penalties on the distribution. An individual can take advantage of this if they are in need of immediate cash for something like an unexpected expense. The distribution is essentially an interest free loan from your retirement account for 60 days. If the money is not available within the 60 days to redeposit, taxes and possible penalties will be assessed on the distribution.
IRS: One 60 Day Rollover in 12 Month Rule
The IRS recognized that individuals were taking advantage of this rule by taking multiple distributions in a single year and therefore increasing the time period. Beginning after January 1, 2015, the IRS changed the law to state that only one rollover can be made from one IRA to another IRA within a 12 month period. This rule does not apply to the following:
rollovers from traditional IRAs to Roth IRAs (conversions)
trustee-to-trustee transfers to another IRA
IRA-to-plan rollovers
plan-to-IRA rollovers
plan-to-plan rollovers
It shows the one rollover in a 12 month period rule was meant to limit the abuse of the 60 day rule because direct rollovers and trustee to trustee transfers are excluded.
What can be Rolled Over?
Most of the time the entire balance in a retirement account can be rolled over to another account unless the balance includes an amount of money that is required to be withdrawn. Examples include required minimum distributions and contributions in excess of limits (plus earnings on the excess contributions). For retirement plans, in addition to RMD's and excess contributions, any loans outstanding at the time of rollover or hardship distributions taken during the year will be subject to taxes and possible penalties.
Are Taxes Assessed at the Time of Distribution?
Distribution from an IRA: Typically, a tax is not assessed on a distribution from an IRA unless the account owner elects to have taxes withheld. A distribution from a pre-tax IRA account is typically subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty if taken before 59 ½.
Distribution from Retirement Plan: Any distribution taken from a retirement plan where cash is made available to the owner is subject to a minimum 20% federal withholding. For example, if you request a $10,000 distribution, you will receive $8,000 and $2,000 will go to the government. There is no option to opt out of this withholding even if you intend to rollover the balance within 60 days. For this reason, a direct rollover would be a way to avoid the 20% withholding.
It is important to understand if you intend to rollover a distribution from a retirement account that the entire amount of the distribution must be redeposited within 60 days to avoid taxes and penalties even if taxes were already withheld. Using the previous example, if you take a $10,000 distribution from a retirement account and have the 20% withheld for taxes you must redeposit $10,000 within 60 days even though you only received $8,000 in cash. This scenario may appear that you are losing $2,000 but when you complete your taxes the $10,000 distribution will not be taxable as long as the full amount was redeposited within 60 days. When you file your taxes, the $2,000 will be included in the federal taxes withheld which is how the money is recouped.
How is the Rollover Reported to the Government?
Any time you wish to utilize the 60 day rule, it is important you keep documentation. Any distribution from a retirement account will generate a 1099-R form that must be reported as income on your tax return. Also, the 1099-R will show any taxes withheld from the distribution. You will receive a 1099-R even if a direct rollover or trustee to trustee transfer was done. The way the distribution is coded determines how the IRS treats it for tax purposes. If the distribution is coded as a direct rollover or trustee to trustee transfer, the distribution will not be treated as taxable income. If the distribution gave you access to cash, the 1099-R will be coded in a way that treats the distribution as a taxable event. If you redeposited the amount into another retirement account within 60 days, it is important you notify your tax preparer and bring documentation showing the deposit was made timely. The tax preparer should then treat the distribution as a non-taxable event.
About Rob.........
Hi, I'm Rob Mangold. I'm the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.